Step into the sizzling world of fast food, where juicy burgers and snappy hot dogs reign supreme! In this mouth-watering journey through history, we uncover the secret sauce behind these quintessential American bites. These humble yet irresistible dishes have not only conquered taste buds in the United States but have taken the world by storm. Ever wondered where hamburgers and hot dogs got their start? Prepare to be amazed as we trace their roots from the kitchens of European immigrants to the bustling streets of early America. Who knew that these simple recipes would one day become global icons?
The Fast-Food Revolution

The 20th-century Fast Food Revolution in the US was a tantalizing mix of economics, convenience, and culinary culture. Economically, the aftermath of World War II ushered in a period of unprecedented prosperity. Increased disposable income of the American middle class made dining out more affordable, and the growth of the automobile industry allowed for easy mobility, paving the way for drive-thru restaurants and highway-side diners to flourish.
Socially, fast food was tailor-made for busy urban lifestyles and the era of dual-income households, where time for home cooking was scarcer than ketchup on a burger.
Culturally, fast food became emblematic of American culinary fusion. Hamburgers and hot dogs, initially rooted in German and European traditions, were adapted, streamlined, and mass-produced. The Fast Food Revolution didn't just fill bellies; it left an indelible mark on American culture, blending prosperity, fast-paced living, and a side of fries.
The Origin Story
The origins of hamburgers and hot dogs are a delicious tapestry woven from diverse immigrant threads in the United States, transforming traditional European sausages and ground meat dishes into iconic American treats.

Hamburgers can be traced back to the German city of Hamburg, where minced beef was a popular dish. Yet, it wasn't until the late 19th century when German immigrants brought their "Hamburg-style" minced beef patties to America that the modern hamburger began to take shape.

The addition of a bun, often credited to Charles Nagreen at the 1885 Seymour Fair, was a game-changer. Lesser-known fact: During World War I, hamburgers were renamed "liberty sandwiches" to curb anti-German sentiment.
Hot dogs, or frankfurters, owe their origin to Frankfurt, Germany. Immigrants from Frankfurt introduced these sausages to the United States in the 1800s. They eventually became "hot dogs" when vendors at baseball games started selling them in rolls. A lesser-known tidbit: the longest hot dog ever made measured a staggering 668 feet!
Both hamburgers and hot dogs have evolved over time, with countless regional variations, toppings, and condiments that reflect the rich cultural tapestry of America. Today, these beloved creations are not just culinary delights but symbols of the nation's immigrant history and culinary innovation.
The Birth Of The Fast Food Industry
The birth of the fast-food industry marked a culinary revolution that forever changed the way Americans dine. At the forefront of this transformation were two iconic chains: White Castle and McDonald's.
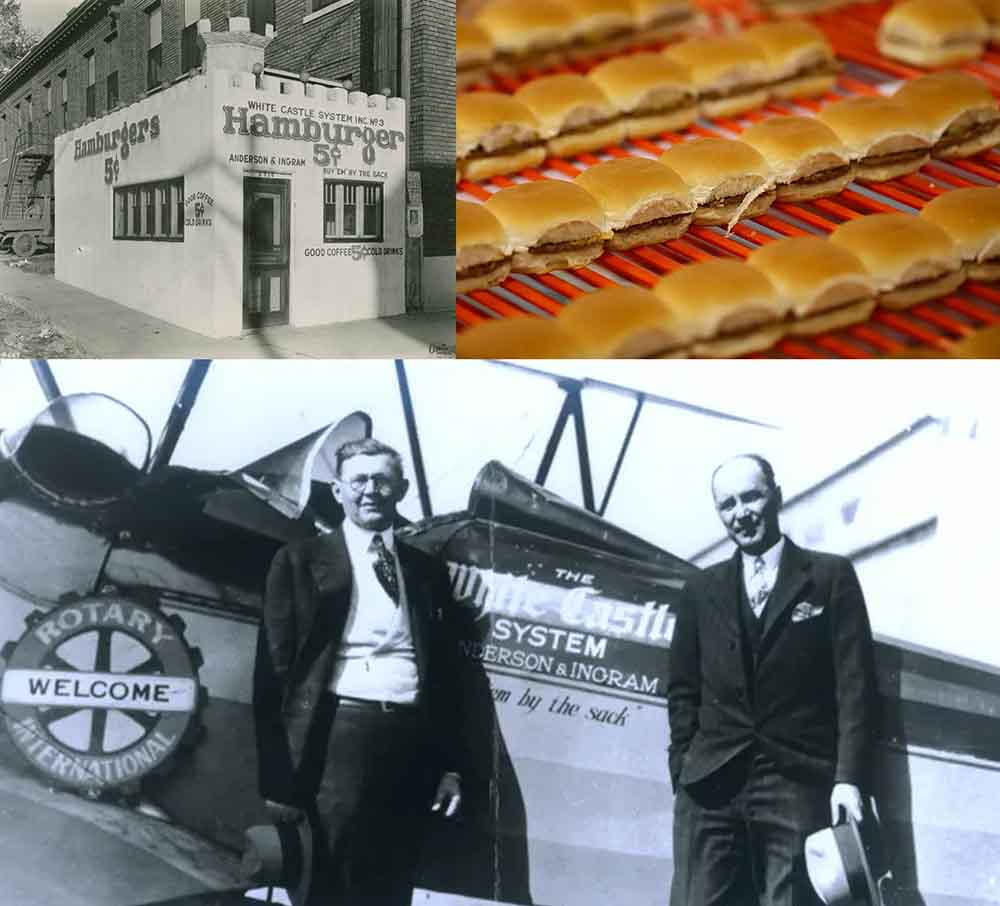

White Castle, founded in 1921 by Billy Ingram and Walter Anderson, pioneered the concept of fast food with a focus on speed, consistency, and affordability. They introduced the world to the slider, a small, square hamburger that could be prepared quickly using their ingenious assembly line cooking technique. This approach became the blueprint for the fast-food industry, emphasising efficiency through technology and innovation.
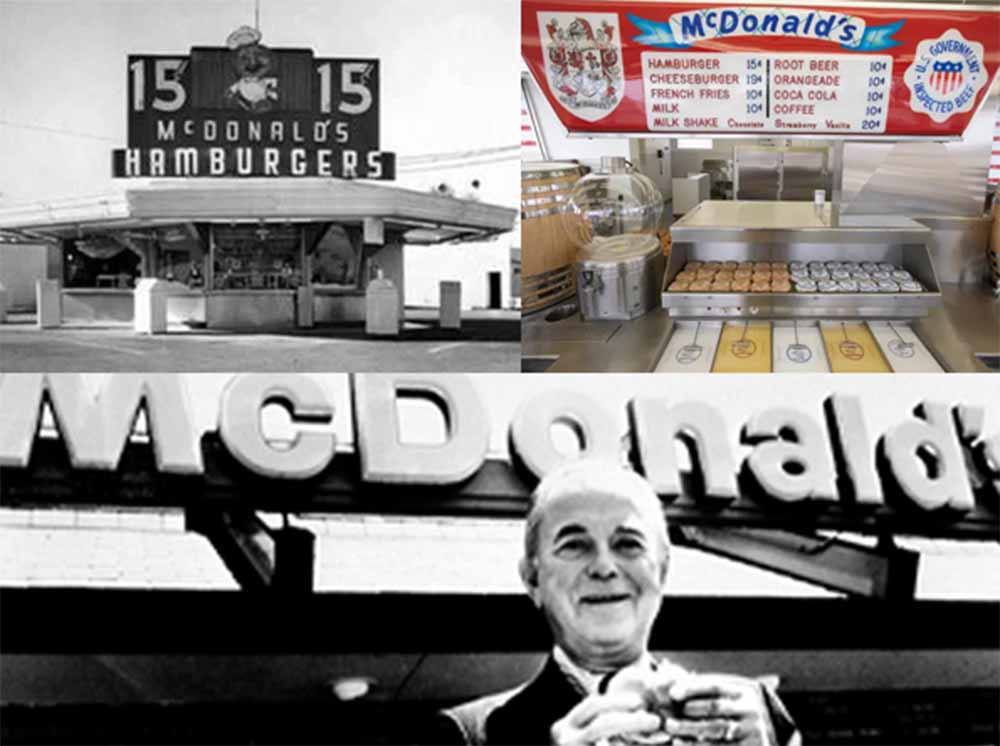

McDonald's, founded by Ray Kroc in 1955, took the fast-food concept a step further by implementing a streamlined production system that prioritised consistency. The "Speedee Service System" used precise measurements and cooking times, ensuring that every burger tasted the same, whether in California or New York. It was a game-changer, and the golden arches soon became synonymous with fast, reliable, and tasty hamburgers.

In the realm of hot dogs, these beloved sausages became deeply intertwined with American leisure and entertainment. From their inception at Coney Island in the early 20th century to becoming a ballpark staple, hot dogs have been a symbol of fun and indulgence. Iconic brands like Nathan's Famous and Oscar Mayer played significant roles in popularising hot dogs. Interestingly, the famous phrase "As American as apple pie" could easily be replaced with "As American as a hot dog at the ballpark," emphasising their enduring popularity.
Fast Food And American Culture

Fast food's impact on American culture is multifaceted, encompassing eating habits, advertising, health debates, and even political symbolism. Fast food's advertising strategies have been pioneering, leveraging catchy jingles and memorable mascots to captivate audiences, especially children. This influence extends to popular culture, with fast food becoming synonymous with American iconography. However, the fast food industry has also faced backlash due to concerns over its role in the ‘obesity epidemic’ and the nutritional quality of its offerings. Documentaries like "Super Size Me" have fueled debates on these issues, pushing fast-food companies to adapt their menus and practices.
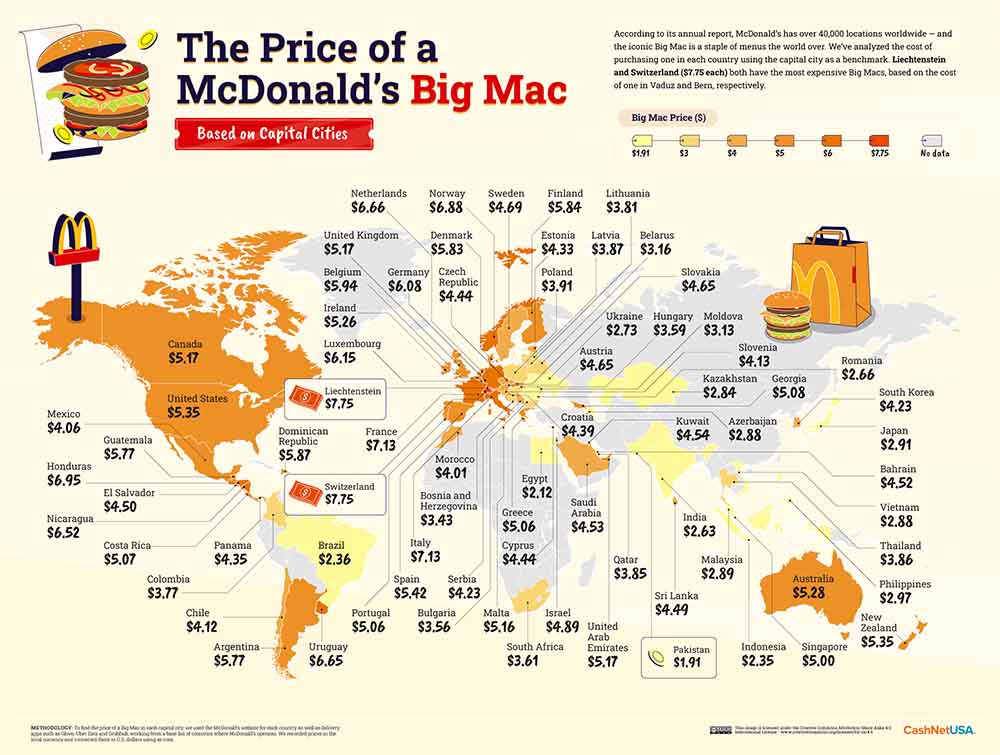
Surprisingly, fast food has also found its way into American politics, with politicians occasionally using it as a symbol of economic success or cultural identity. For instance, the "Big Mac Index" is a light-hearted economic indicator measuring currency valuation through the price of a Big Mac.
Challenges And Controversies

The fast food industry has faced a barrage of challenges and controversies.
1. The "Fight for $15" movement in the United States has been advocating for a $15 minimum wage for fast food workers, citing low wages and inadequate benefits as critical issues. Several lawsuits and protests have occurred against major fast food chains, such as McDonald's and Burger King, regarding alleged labour rights violations.
2. Sustainability issues are paramount, as the industry contributes significantly to food waste, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Public health debates persist as fast food is linked to rising obesity rates and related health problems. A report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) links high consumption of fast food to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease in the United States. According to the World Obesity Federation, as of 2021, nearly 79 million adults in India are estimated to be living with obesity, partially attributed to fast food consumption.
India And Fast Food

By embracing regional flavours and dietary restrictions, fast food giants successfully navigated globalization. The ascent of American fast food in India is a captivating narrative, emblematic of evolving tastes and lifestyle shifts. This journey commenced in the late 20th century when McDonald's made its Indian debut in 1996 through strategic partnerships with local businesses. To cater to local palates and respect cultural norms, they innovated by introducing items like the vegetarian-friendly McAloo Tikki while eliminating beef entirely. Simultaneously, Indian fast-food chains like Domino's and Cafe Coffee Day ventured into the market, offering their interpretations of American fast food with a desi twist. India's economic liberalisation during the early '90s spurred rising incomes, urbanisation, and a burgeoning middle class, fostering a greater appetite for convenient dining. Aggressive marketing and branding campaigns by American chains positioned them as symbols of modernity and aspiration.