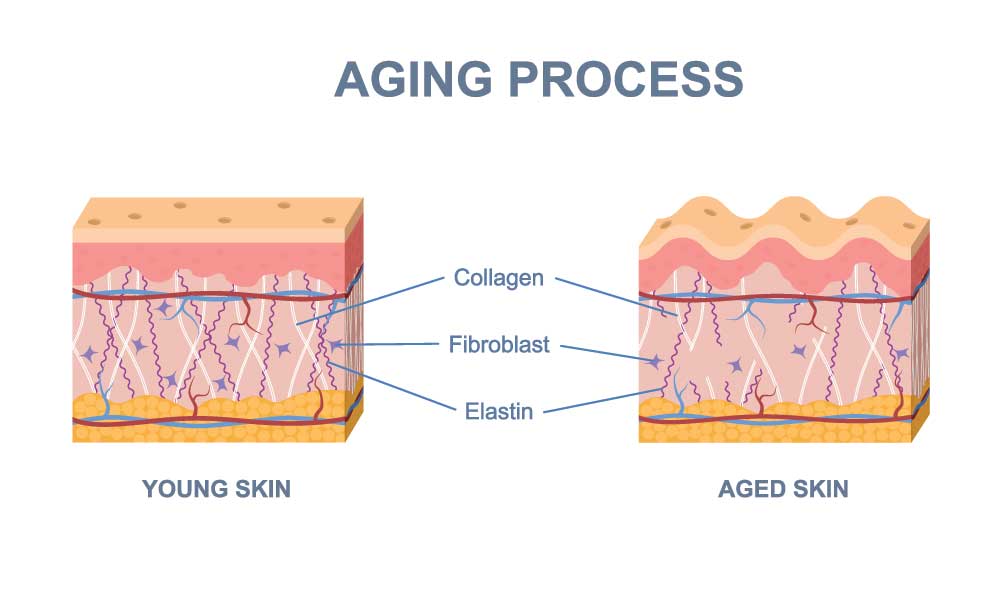
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein composed of amino acids, primarily glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. It acts as a building block for the skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments. In the skin, collagen is found in the middle layer or dermis, forming a fibrous network that supports the skin's structure.
The Role Of Collagen In Skin Health
- Structural Support: Collagen provides structural integrity to the skin, giving it strength and firmness. This support helps maintain the skin's shape and prevents it from sagging. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to a loss of skin firmness and the formation of wrinkles.

- Hydration: Collagen helps retain moisture in the skin, keeping it hydrated and plump. The protein interacts with hyaluronic acid, another key component in the skin, to maintain hydration levels. Proper hydration is essential for a healthy, radiant complexion and prevents the skin from becoming dry and flaky.
- Healing And Regeneration: Collagen plays a critical role in wound healing and skin regeneration. When the skin is injured, collagen production increases to repair damaged tissue. This process helps close wounds and restore the skin's integrity. Additionally, collagen aids in the turnover of skin cells, ensuring that the skin remains fresh and rejuvenated.
- Barrier Function: Collagen contributes to the skin's barrier function, protecting it from external pollutants, bacteria, and toxins. A strong collagen network ensures that the skin remains resilient against environmental damage and reduces the risk of infections and irritations.
Factors Affecting Collagen Production
Several factors can affect collagen production in the skin, including:


- Smoking: Smoking decreases collagen production and damages existing collagen, leading to premature skin ageing. The chemicals in tobacco smoke reduce blood flow to the skin, impairing nutrient delivery and collagen synthesis.
- Diet: A poor diet lacking in essential nutrients can hinder collagen production. Vitamin C, in particular, is crucial for collagen synthesis. Without adequate vitamin C, the body cannot produce or maintain collagen effectively.
- Stress: Chronic stress increases the production of cortisol, a hormone that breaks down collagen in the skin. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and a healthy lifestyle can help preserve collagen levels.
Enhancing Collagen Levels
- Topical Treatments: Skincare products containing retinoids, peptides, and antioxidants can stimulate collagen production and protect existing collagen from damage. These ingredients boost the skin's natural repair processes and enhance its structural integrity.
- Collagen Supplements: Oral collagen supplements, typically derived from animal or marine sources, can help increase collagen levels in the skin. Studies suggest that these supplements improve skin elasticity, and hydration, and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins and minerals supports collagen production. Foods like bone broth, fish, citrus fruits, leafy greens, and berries are excellent for boosting collagen synthesis.
- Sun Protection: Protecting the skin from UV radiation is crucial for maintaining collagen levels. Wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, staying in the shade whenever possible, and wearing protective clothing can prevent collagen breakdown caused by sun exposure.
- Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, staying hydrated, and managing stress can significantly impact collagen production and overall skin health.